Jul 20 2011
Fabian Flöck gave an interesting talk on the topic “Towards a diversity-minded Wikipedia” at the ACM 3rd International Conference on Web Science in Koblenz, Germany. You can find his talk on VideoLectures.net as well as in our presentations section. The corresponding paper can be downloaded here.
Towards a diversity-minded Wikipedia
Watch this on VideoLectures.net
Jun 27 2011
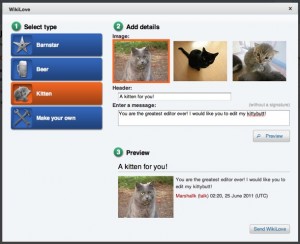 Wikipedia is introducing the WikiLove Button. It is already live on the Wikipedia test site and it will be available site-wide on Wednesday June 29th. It appears in the right hand corner of each user’s page, in the form of a little red heart. Users are encouraged to click the button when they come across edits or other on-site activity that deserves commendation.
Wikipedia is introducing the WikiLove Button. It is already live on the Wikipedia test site and it will be available site-wide on Wednesday June 29th. It appears in the right hand corner of each user’s page, in the form of a little red heart. Users are encouraged to click the button when they come across edits or other on-site activity that deserves commendation.
A click of the button will result in the launch of a Love Interface, in which the user is presented a number of options for what kind of love to send and images to append to a free-text compliment area. The resulting declaration of support is published to the receiving user’s account discussion page and is monitored by top Wikipedia users to prevent misuse.
Jun 07 2011
 Ontotext announced the release of OWLIM version 4.0 (beta). OWLIM 4.0 is a major development for the OWLIM family of RDF Databases and offers a number of fundamental changes aimed at better differentiation between the editions of the product as well as some important new features and enhancements.
Ontotext announced the release of OWLIM version 4.0 (beta). OWLIM 4.0 is a major development for the OWLIM family of RDF Databases and offers a number of fundamental changes aimed at better differentiation between the editions of the product as well as some important new features and enhancements.
With this release, Ontotext have rebranded their line of OWLIM editions and introduced a new member of the family:
- OWLIM Lite is the new name of SwiftOWLIM
- OWLIM SE (Standard Edition) is the new name of BigOWLIM; it is positioned as a single-server product,
- OWLIM Enterprise is an extension of OWLIM SE, which includes the Replication Cluster capabilities. It is priced and sold as a separate product intended for scalable, high-resilience, mission-critical installations, offering extended online re-configuration and other features which improve manageability
Scalability to 1 trillion nodes: A brand new indexing mechanism has been developed for OWLIM SE that uses a configurable bit-size for internal identifiers of nodes in the RDF graph (URIs, blank nodes and literals). For very large datasets, the bit-size can be set to 40 bits, allowing up to 1 trillion unique entities to be stored.
Faster SPARQL 1.1 Query support: Thanks to Ontotext’s investment in development resource for the Sesame project, all OWLIM editions now boast support for this evolving SPARQL standard. While handling of SPARQL 1.1 through Jena was fast enough to allow OWLIM to get excellent scores in the latest BSBM evaluation, using SPARQL 1.1 through Sesame makes it even faster and available in all editions of OWLIM. SPARQL 1.1 Query specification offers new features such as: Aggregates, Subqueries, Negation, Expressions in the SELECT clause, Property Paths, Assignment, Short form for CONSTRUCT and an expanded set of functions and operators. Federation will be supported in a subsequent release.
Easy server deployment: every edition of OWLIM includes re-packaged Sesame Web applications for easy deployment of OWLIM servers. Now OWLIM can be deployed simply by copying a WAR file. New OWLIM repository instances can be created using the Sesame Workbench UI administration tool.
There are number of other new features for specific editions:
- OWLIM SE now provides a remote notification mechanism that includes transaction information.
- Performance analytics: OWLIM SE provides information on cache utilization and behaviour through a JMX interface. This feature can be useful when investigating loading behaviour and query performance.
- OWLIM Lite is now packaged as a single jar file, with a simpler free-for-use licensing scheme.
Note: This beta release can not be used with existing OWLIM storage files. The full release due in couple of weeks time will include an automatic upgrade facility for updating files created using previous versions.
More information on OWLIM can be found here: http://www.ontotext.com/owlim
May 19 2011
In the Spiegel Online article from March 3rd, 2011 author Konrad Lischka talks about Facebook, Twitter and Co’s algorithms to filter all displayed content. So it could happen that posts from friends will never be shown for you on Facebook as the algorithm identifies these posts as irrelevant. Or worse, friends that have been added will disappear as will their posts. Users of social platforms often only realize the fact that algorithms decide what they see after months and therefore they feel patronized and not informed.
The algorithm determines from previously visits to profiles and pages, the number of comments a user creates, user’s visits to profiles/pages etc. how relevant a post is. Simply said, people that like cats will no longer see photos of dogs but are rather presented with pictures and posts from other cat-lovers. Doesn’t sound that bad, but it might become a problem when people use social platforms more and more as their primary sources to get news and opinions. Irrelevant or contrary opinions are simply not displayed and that can create a wrong picture of the world.
Eli Pariser, former Executive Director of MoveOn.org, and the organization’s current Board President, talks about a world where we only see things on the Web of which algorithms have decided that we must see these things – but we will not see what we should see. The article’s author raises another problem: It may seem plausible that people in a specific environment hold back with their opinions. If that happens we lack a different viewpoint – and the digital world seems much more unanimous than it truly is.
Jan 14 2011
Wikipedia ist nicht nur ein Nachschlagewerk, sondern auch eine Datenbank der Informationen. Mit semantischen Techniken versuchen Forscher den Wissensschatz zu heben.
Lesen Sie den ganzen Artikel hier: URL| Download PDF (No hits, 92.73 kB)

 Subscribe to RENDER news
Subscribe to RENDER news Follow us on Twitter
Follow us on Twitter  RENDER on Facebook
RENDER on Facebook





 learn more
learn more
